The scope of the SMTP proxy is to control and optimize SMTP traffic in general and to protect your network from threats when using the SMTP protocol. The SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol) protocol is used whenever you send an e-mail through your mail client to a remote mail server (outgoing mail). It will also be used if you have your own mail server running on your LAN (GREEN interface) or your DMZ (ORANGE interface) and are allowing mails to be sent from the outside of your network (incoming requests) through your mail server.
Warning
In order to download mail from a remote mailserver with your local mail clients, the POP3 or IMAP protocol will be used. If you want to protect that traffic too, you have to use the POP3 proxy. Scanning of IMAP traffic is currently not supported.
With the mail proxy functionality, both sorts of traffic (incoming and outgoing mail) can be scanned for virii, spam and other threats. Mail will be blocked if necessary and notices will be sent to both the receiving user and the administrator. With the possibility to scan incoming mail, the mail proxy can handle incoming connections and pass the mail to one or more internal mail servers in order to remove the necessity to have SMTP connections from the outside within your local networks.
The following is a complete feature list, which will be described in detail in the following sections:
Multi-domain support
Configurable relaying policy per domain
Spool visualiation & managment
External authentication support
TLS Email Transport Encryption support
Mail statistics
Day, Week, Month, Year graphs
Spam, Virus, Bounced, Rejected
Configurable maximum mail data size
Spam blocking
Spam notification
Local/Remote Quarantine
Realtime Blacklist (RBL) support
Custom Client/Sender/Recipient black/whitelists
Content-matching rules, DNS-based, checksum-based and statistical filtering
Auto learning / Training
Subject and header modification on spam
Greylisting support
Virus scanning
Virus notification
Local/Remote Quarantine
Extension blocking
Notification
Block banned files
Double extension blocking
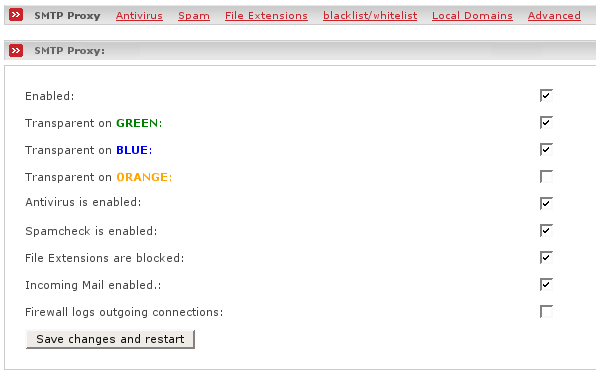
- Enabled
This enables the SMTP proxy in order to accept requests on port 25.
Note
Relaying is disabled without authentication in non transparent mode.
- Transparent on zone
If the transparent mode is enabled, all requests to destination port 25 will be intercepted and forwarded to the SMTP proxy without the need of any special configuration changes on your clients.
- Antivirus is enabled
Tick this on if you'd like to enable the antivirus. If you enable the antivirus, you can configure the antivirus by clicking on the Antivirus link. See the section called “Antivirus” for a detailed description.
- Spamcheck is enabled
Tick this on if you'd like to enable the antispam. If you enable the spam filter, you may configure it by clicking on the Spam link. See the section called “AntiSpam” for a detailed description.
- File Extension are blocked
Tick this on if you like to enable the file extension blocker. With this you may specify a list of file extensions which are not allowed as attachement. If you enable it, configure it by clicking on the File Extensions link. See the section called “Banned File Extension” for a detailed description.
- Incoming Mail enabled
If you have an internal Mailserver and would like the SMTP proxy to forward incoming mails to your internal server you need to tick this checkbox on.
Note
You need to configure the e-mail domains for which it should be responsable. List the responsable domains within the page you reach by clicking on the Domains link. See the section called “Domains” for a detailed description.
- Firewall logs outgoing connections
Tick this on if you want the firewall to log all established outgoing connections. Note that in some countries this may be illegal.
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP proxy by pushing this button.
The Antivirus is a core functionality of the SMTP proxy module. It knows four different possibilities to handle mail containing a virus. You have also the possibility to configure an email address for notification of the recognized and handled threat.
The antivirus section provides the following configuration options:
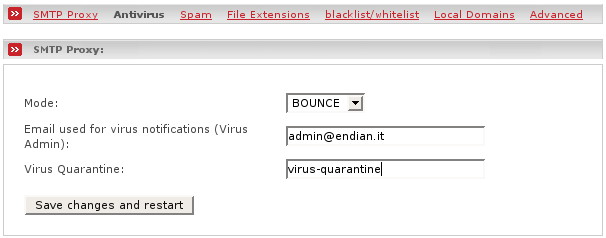
- Mode
This allows you to select the mode of handling infected emails. The following possibilities exist:
- DISCARD
In this mode the email will not be delivered to its recipients and deleted without sending a notification to the sender. If a virus quarantine is defined a copy of the original e-mail will be sent or copied to the virus quarantine.
Note
In most cases this is the best way of handling infected mails.
- BOUNCE
In this mode the email will not be delivered to its recipients but bounced back to the sender in form of a delivery status notification with a non-delivery notification. If a virus quarantine is defined a copy of the original email will be sent or copied to the virus quarantine.
Warning
Sending notification mails to the sender is insofar not really helpful as worms normally use spoofed sender addresses. Therefore such notifications mostly will reach anyone but the right person. The SMTP proxy does not send bounces back to the sender if a worm, of which the SMTP proxy knows that it normally spoofs the sender address, will be recognized. Nevertheless the benefit may be less than the problems caused by this mode.
- REJECT
The email will be rejected by the MTA. Basically this is the same as BOUNCE. (removed in version 2.1)
- PASS
Mail will pass to its recipients, regardless of bad content.
- Virus Admin
Gives you the possibility to specify a (fully qualified) administrator email address where virus notifications should be sent. (Default is empty)
- Virus Quarantine
Location to put infected mail into. The following possibilites are valid:
- leave empty
Disables the quarantine
- virus-quarantine
Set this if you would like to store infected mails on the firewall. You will find the mails in /var/amavis/virusmails/. This is the default.
Warning
There is no possibility to control and manage the quarantine if you use this possibility.
- any email address
You can specify any valid e-mail address, to which infected e-mails will be forwarded to. With this variant you can forward all infected mails to a POP3 or an IMAP account where you may manage them easily.
Note
The email address must contain a @.
Warning
This email address must not have any virus scanner, otherwise the quarantined mail will be blocked by that server.
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button.
The antispam module knows several different possibilities to protect you against spam. In general spamassassin and amavisd-new are used to filter out spam. SpamAssassin incorporates several means of detecting spam. It has a “score tally” system where large numbers of inter-related rules fire off and total up a score to determine if a message is spam or not. In this system each rule affects the proper score of every other rule in the ruleset and the system tries to balance the most spam and nonspam each on the right side of the tolerance mark.
While much of the rules block much of simplier spam, well known spam and spam sent by known spam hosts, spammer always adapt their messages in order to knock out spam filters. Therefore it is necessary to also always train the spam filter in order to reach a personalized and stronger statistical filter (bayes).
Note
While the spam filter blocks much spam it never will block all of your spam.
Note
The spamassassin rules will not be updated automatically like the virus signatures. Here you can read why.
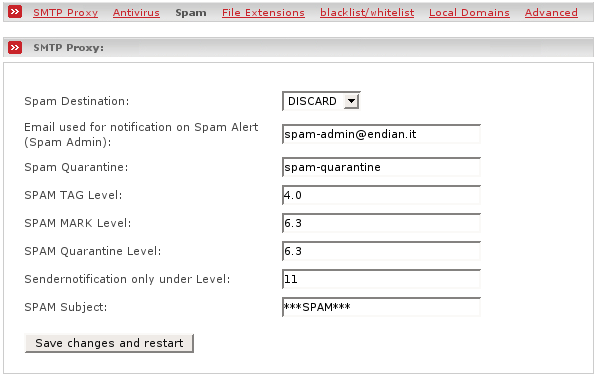
- Spam destination
This allows you to define what should be happen to spam mails. The following possibilities do exist:
- DISCARD
In this mode the email will not be delivered to its recipients and deleted without sending a notification to the sender. If a spam quarantine is defined a copy of the original e-mail will be sent or copied to the spam quarantine.
Note
In most cases this is not very useful, since it is possible that the spam filter may block also regular mail (false positives) if it is configured to restrictive.
Warning
Check your local law. In most countries it is illegal to delete mail without the permission of the recipient.
- BOUNCE
In this mode the email will not be delivered to its recipients but bounced back to the sender in form of a delivery status notification with a non-delivery notification. If a spam quarantine is defined a copy of the original email will be send or copied to the spam quarantine.
Warning
Sending notification mails to the sender of spam is insofar not really helpful as spammers then more than ever know that they hit a real e-mail address. Furthermore, spammers mostly do not use their real sender addresses. They nearly always use spoofed sender addresses, therefore such notifications always reach anyone but the right person.
- REJECT
The email will be rejected by the MTA. Basically this is the same as BOUNCE. (removed in version 2.1)
- PASS
Mail will pass to its recipients, regardless of bad content.
Note
In most cases, this is the best mode you can use. The spam filter adds spam headers and changes the subject of the mail if it recognizes the mail as spam. The recipients then may use their mail clients to filter those mails themselves.
- Spam admin
Gives you the possibility to specify a (fully qualified) administrator e-mail address to which spam notifications should be sent. (Default is empty)
- Spam quarantine
Location to put spam mail into. The following possibilities are valid:
- leave empty
Disables the quarantine
- spam-quarantine
Set this if you would like to store spam mails on the firewall. You will find the mails in /var/amavis/virusmails/. This is the default.
Warning
There is no possibility to control and manage the quarantine if you use this possibility.
- any email address
You can specify any valid email address, to which spam mail will be forwarded. With this variant you can forward all spam mails to a POP3 or IMAP account where you may manage them easily.
Note
The email address must contain a @.
Warning
This email address must not have any blocking spam filter, otherwise the quarantined mail will be blocked by that server.
- SPAM TAG Level:
If spam score is greater or equal to this level add spam info e-mail headers. You will find them as X-Spam-Status and X-Spam-Level headers.
Note
This level will not block the mail regardless what you defined as spam destination.
Example 7.9. Example spam info headers
X-Spam-Status: No, score=-1.54 tagged_above=-4 required=6.31 tests=[AWL=-0.723, BAYES_00=-2.599, HTML_80_90=0.146, HTML_FONT_SIZE_NONE=0.033, HTML_FONT_SIZE_TINY=0.533, HTML_FONT_TINY=0.964, HTML_IMAGE_RATIO_04=0.105, HTML_MESSAGE=0.001] X-Spam-Score: -1.54 X-Spam-Level:
- SPAM MARK level
If spam score is greater or equal to this level, mark the mail as spam by tagging the subject line with *** SPAM *** and add the X-Spam-Flag header.
Note
This level will not block the mail regardless what you defined as spam destination.
Example 7.10. Example spam info headers
X-Spam-Status: Yes, hits=12.4 tagged_above=-10.0 required=5.3 tests=BAYES_99, RCVD_HELO_IP_MISMATCH, RCVD_IN_XBL, RCVD_NUMERIC_HELO, SARE_FWDLOOK, SARE_MONEYTERMS, SARE_OEM_FAKE_YEAR X-Spam-Level: ************ X-Spam-Flag: YES
Note
Users may use X-Spam-Flag: YES as search string for their mail client filter.
- SPAM quarantine level
If spam score is greater or equal to this level then the spam evasive action which you selected in spam destination will be used.
Note
This is the level which may delete spam mail if you selected to DISCARD spam mail.
- Sendernotification only below level
If spam score is greater than this level no notification mails will be sent to the administrator.
- SPAM subject
String to prepend to the subject header field when message exceeds SPAM MARK level.
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button.
Greylisting is a simple method of defending electronic mail users against e-mail spam. In short, a mail transfer agent which uses greylisting will temporarily reject any e-mail from a sender it does not recognize. The sender will be delayed for the configured time. If the mail is legitimate, the originating server will try again to send it later. If the delay time is elapsed, the destination will accept it. Spammers normaly will not retry to send temporarily rejected mails, since this is cost effective. However, even spam sources which re-transmit later are more likely to be listed in DNSBLs and distributed signature systems such as pyzor.
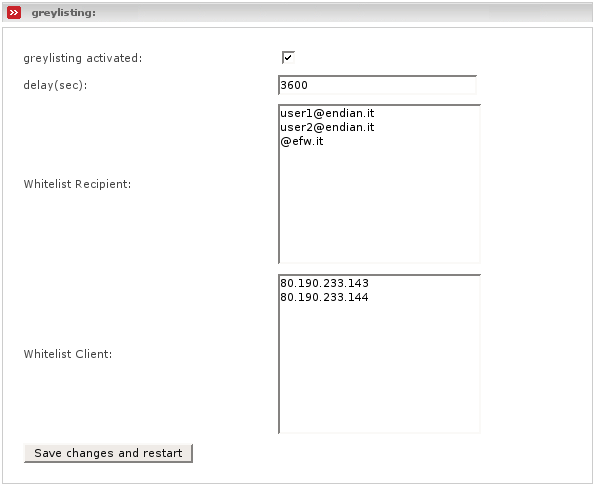
- greylisting activated
Tick this on if you want to enable greylisting.
- delay(sec)
You can change the delay from 30 secs to maximum 3600 (1 hour).
- Whitelist recipient
With this you can whitelist an address or a complete domain (one entry per line).
- Whitelist client
You can exclude a Mailserver address in order to bypass greylisting for this mail server (one entry per line).
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button
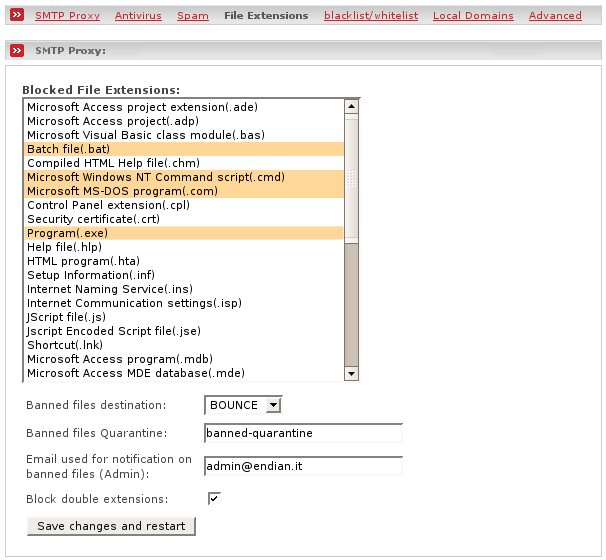
This allows you to block files with certain file extensions which may be attached to mails. Mails which contain such attachements will be recognized and the selected action will be performed for the respective mail.
- Blocked File Extensions
You can select one or more file extensions. In order to select multiple files press the control key and select the desired entries with your mouse.
Note
File Extension Block must be enabled in gereral settings.
- Banned files destination
This allows you to define what should happen to e-mails containing files with banned extensions. The following possibilities do exist:
- DISCARD
In this mode the e-mail will not be delivered to its recipients and deleted without sending a notification to the sender. If a quarantine for banned files is defined a copy of the original e-mail will be sent or copied to that quarantine.
- BOUNCE
In this mode the e-mail will not be delivered to its recipients but bounced back to the sender in form of a delivery status notification with a non-delivery notification. If a quarantine for banned files is defined a copy of the original e-mail will be sent or copied to that quarantine.
Note
Normaly it may be wise to use this variant, since senders then know what they are doing wrong.
- REJECT
The e-mail will be rejected by the MTA. Basically this is the same as BOUNCE. (removed in version 2.1)
- PASS
Mail will pass to its recipients, regardless of bad content.
- Banned files quarantine
Location to put mail with banned files into. The following possibilites are valid:
- leave empty
Disables the quarantine
- spam-quarantine
Set this if you would like to store bad mails on the firewall. You will find the mails in /var/amavis/virusmails/. This is the default.
Warning
There is no possibility to control and manage the quarantine if you use this possibility.
- any email address
You can specify any valid e-mail address, to which bad mail will be forwarded. With this variant you can forward all bad mail to a POP3 or an IMAP account where you may manage it easily.
Note
The e-mail address must contain a @.
- Admin notification
Gives you the possibility to specify a (fully qualified) administrator e-mail address where notifications about bad attachements should be sent. (Default is empty)
- Block double extension:
tick this if you want block attachements which have one of the following double extensions.
filename.XXX.exe
filename.XXX.vbs
filename.XXX.pif
filename.XXX.scr
filename.XXX.bat
filename.XXX.cmd
filename.XXX.com
filename.XXX.dll
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button.
An often used method to block certain types of spam e-mails are so called real-time blacklists (RBL). Those have been created by many different organisations and will be managed, administrated and actualised by them. If a domain or a sender ip address is listed within one of those blacklists, the mail will be refused promptly and without the need and possibility to gather more information about it. This saves more bandwith in comparison to the RBL of the antispam module, since the mail will not be accepted and then handled, but refused as soon as a listed ip address will be recognized.
This dialogue gives also the possibility to explicitely block (blacklist) or explicitely allow (whitelist) certain sender, recipients, ip addresses or networks.
A DNS-based Blackhole List (DNSBL, Real-time Blackhole List or RBL), is a published list of IP addresses, in a format that can be easily queried by computer programs on the Internet. As the name suggests, the technology is built on top of the Internet DNS or Domain Name System. DNSBLs are chiefly used to publish lists of addresses linked to spamming.
Warning
It may happen that IP addresses have been wrongly listed by the RBL operator. If this should happen, it may negatively impact your communication, to the effect that mail will be refused without the possibility to recover it. You also have no direct influence on the RBLs.
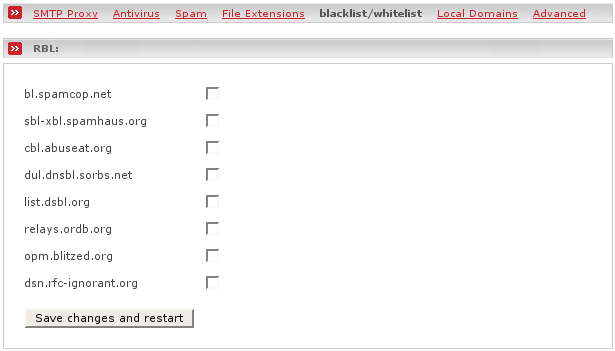
- bl.spamcop.net
RBL based on user submission.(www.spamcop.net)
- sbl-xbl.spamhaus.org
The SBL is a realtime database of IP addresses of verified spam sources (including spammers, spam gangs and spam support services), maintained by the Spamhaus Project team and supplied as a free service to help e-mail administrators to better manage incoming e-mail streams.
The Spamhaus Exploits Block List (XBL) is a realtime database of IP addresses of illegal 3rd party exploits, including open proxies (HTTP, socks, AnalogX, wingate, etc), worms/viruses with built-in spam engines, and other types of trojan-horse exploits (www.spamhaus.org).
- cbl.abuseat.org
The CBL takes its source data from very large spamtraps, and only lists IPs exhibiting characteristics which are specific to open proxies of various sorts (HTTP, socks, AnalogX, wingate etc) which have been abused to send spam, worms/viruses that do their own direct mail transmission, or some types of trojan-horse or “stealth” spamware, without doing open proxy tests of any kind.
The CBL does NOT list open SMTP relays (cbl.abuseat.org).
- dul.dnsbl.sorbs.net
This contains a list of Dynamic IP Address ranges (www.au.sorbs.net).
- list.dsbl.org
DSBL is the Distributed Sender Blackhole List, it publishes the IP addresses of hosts which have sent special test email to listme@listme.dsbl.org or another listing address.The main delivery mechanism of spammers is the abuse of non-secure servers. For this reason, many people want to know which servers are non-secure so they can refuse email from these servers. DSBL is intended as a place to publish whether a server is non-secure (www.dsbl.org).
- relays.ordb.org
ORDB.org is the Open Relay Database. ORDB.org is a non-profit organisation which stores a IP-addresses of verified open SMTP relays. These relays are, or are likely to be, used as conduits for sending unsolicited bulk email, also known as spam. By accessing this list, system administrators are allowed to choose to accept or deny email exchange with servers at these addresses (www.ordb.org).
- opm.blitzed.org
OPM is designed to list IPs confirmed to be running insecure proxies. These can be present because of misconfiguration of legitimately-installed software, or they can be due to the installation of trojans, viruses and other malware. OPM differs from other open proxy DNSBLs in that it tries not to proxy test remote hosts unless they are implicated in reports of abuse, and it aggressively expires old IPs, especially those known to be used for dynamic leases, such as dialup customers.
The opm.blized.org does NOT list open SMTP relays (wiki.blitzed.org/OPM). (This list has been removed in version 2.1)
- dsn.rfc-ignorant.org
The dsn.rfc-ignorant.org is a list which contain domains or IP networks whose administrators choose not to obey the RFCs, the building block “rules” of the net (www.rfc-ignorant.org).
- blackhole.securitysage.com
This list is comparable to the dsn.rfc-ignorant.org list - it contains a list of domain names (as opposed to IP addresses) that can be checked against the client domain of an email, as well as the domain portion (after the @) of the sender and recipient addresses. (www.securitysage.com). (New in version 2.1)
- save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button.
Note
advanced users can modify the list by editing the file /var/efw/smtpd/default/RBL.
You have full control and can blacklist, whitelist specific sender/recipient or client.
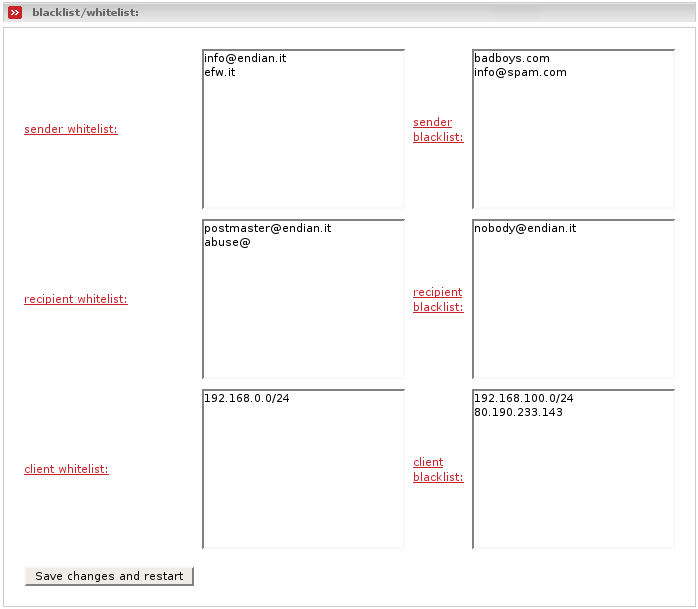
- Sender Whitelist/Blacklist
There are multiple ways to deny (blacklist) or allow (whitelist) a sender or domain (one per line).
The addresses in these listings will be compared to the senders' e-mail address of each incoming mail.
- Domain (with subdomains)
Allow or deny a complete domain with all its subdomains.
This will cover each e-mail address under both domains and its subdomains, like mail@sub.endian.it.
- Subdomains
Allow or deny only the subdomains of the specified domain. In order to achieve this, add a leading dot to the domain name.
This will cover each e-mail address under each subdomain of both domains. For instance it will include mail@test.endian.it but exclude info@endian.it.
- Address
Allow or deny a single fully qualified e-mail address or any e-mail address having the specified user part.
This will cover the single e-mail address info@endian.it of course, and each e-mail address with postmaster or abuse as user part, like postmaster@riaa.org.
- Recipient Whitelist/Blacklist
There are multiple ways to deny or allow a single recipient or domain (one per line).
These addresses covered by this listings will be compared with the recipient's email address of each incoming mail.
- Domain (with subdomains)
Allow or deny a complete domain with all it's subdomains.
This will cover each email address under both domains and its subdomains, like mail@sub.endian.it.
- Subdomains
Allow or deny only the subdomains of the specified domain. In order to achieve this, add a leading dot to the domain name.
This will cover each e-mail address under each subdomain of both domains. For instance it will include mail@test.endian.it but exclude info@endian.it.
- Address
Allow or deny a single fully qualified e-mail address or any e-mail address having the specified user part.
This will cover the single email address info@endian.it of course, and each email address with postmaster or abuse as user part, like postmaster@riaa.org.
Warning
If the SMTP proxy runs in transparent mode, each IP address of subnets known to the Endian Firewall will be allowed automatically. Therefore it is not possible to blacklist a recipient which has one of those ip addresses.
- Client Whitelist/Blacklist
You can also block or allow a single IP address or subnet from which mail will be sent (one per line).
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button.
Note
The whitelist overwrites the blacklists. You can blacklist a whole subnet and then whitelist a single address.
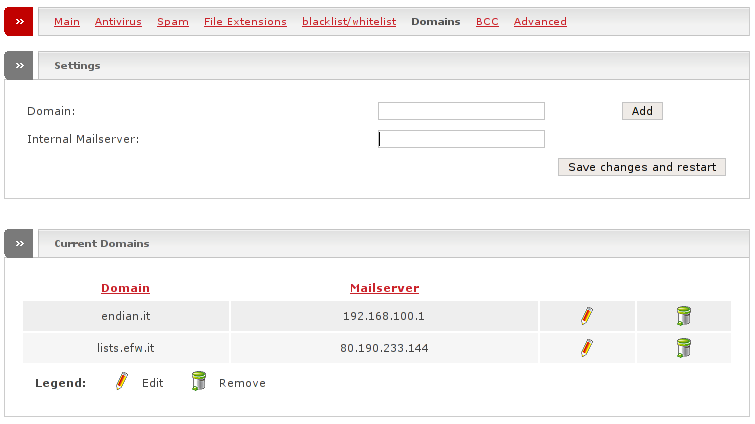
If you have enabled incoming mail and would like to forward that mail to a mail server behind the Endian Firewall - usually set up in the GREEN or ORANGE zone - you need to declare the domains which will be accepted by the SMTP proxy and to which of your mail servers the incoming mail should be forward to. It is possible to specify multiple mail servers behind Endian Firewall for different domains. It is also easily possible to use Endian Firewall as a backup MX.
Note
Incoming mail must be enabled to activate this functionality.
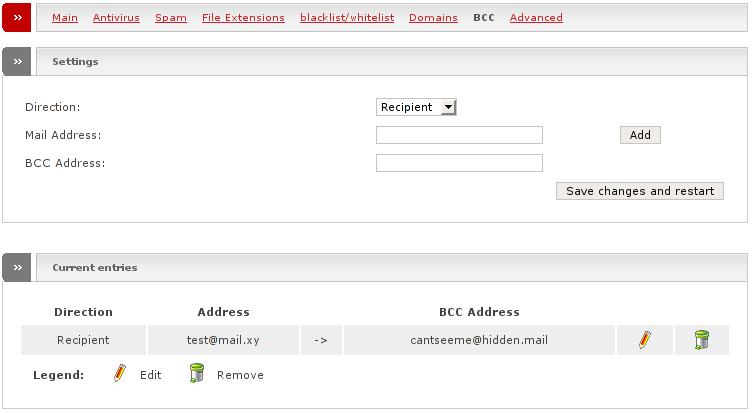
Enable this if you would like to have a copy of certain mails that go through the SMTP proxy - being it to a certain recipient or from a certain sender. Specify if you want to check the e-mail for a recipient- or a sender-address. Then type that e-mail address into the Mail address field and finally add the address that should get the copy in the BCC (Blind Carbon Copy) address field.
Note
The sender and the recipient of the e-mail will not know that their messages have been copied unless you tell them.
Warning
In most countries of this planet it is highly illegal to read other people's private messages. Do not abuse this feature.
This section covers advanced settings of the SMTP proxy.
If you have a dynamic IP address because you are using an ISDN or ADSL dialup internet connection, you will get problems sending mails to other mail servers. More and more mail servers compare DNS with it's reverse DNS, while other mail servers check if your ip address is listed as a dynamic IP address and refuse to accept your e-mail. Therefore it could be necessary to use a smarthost for sending emails.
A smarthost is a mail server which your smtp proxy will use as outgoing SMTP. The smarthost needs to accept your e-mail and relays it for you. Normally you may use your providers SMTP as smart host, since it will accept to relay your e-mails and other mail servers may not.
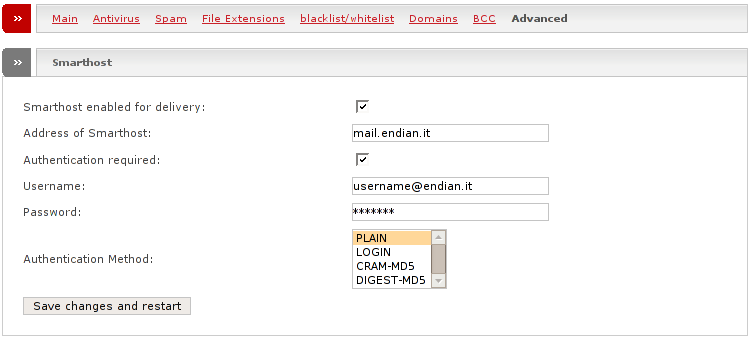
- Smarthost enabled for delivery
Tick this on to send all outgoing mail through the smarthost.
- Address of Smarthost
Outgoing mailserver for final delivery.
Note
Normally you may use your providers SMTP as smart host, since it will accept to relay your mails and other mail servers may not.
- Authentication required
Some mail servers require authentication. Tick this on if your mail server requires authentication.
- Username
Username to use for the authentication.
- Password
Password to use for the authentication.
- Authentication method
Choose the authentication method for your smarthost. Supported types are PLAIN, LOGIN, CRAM-MD5 and DIGEST-MD5.
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button.
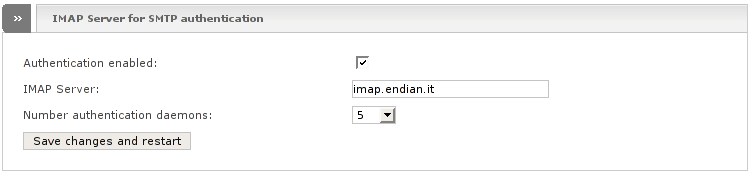
The SMTP Proxy can query a remote IMAP Server to authenticate users. This way it is possible to use the SMTP Proxy from remote with the authentication relayed to any external domain.
- Authentication enabled
Tick this on to enable the remote authentication.
- IMAP Server
Address of the remote IMAP Server.
- Number authentication daemons
If you have many concurrent users you can increase the number of authentication daemons (default 5).
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button.
There are even more advanced configuration possibilities for the SMTP proxy. You may change the maximal size of a single email address, change the language of smtp proxy mails, or make the mail server more restrictive and strictly RFC compliant in order to fight against spam.
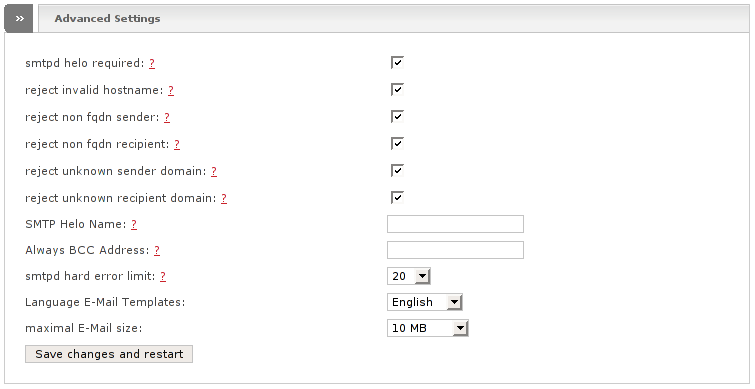
- Smtpd helo required
If this is enabled the connecting client must send a HELO (or EHLO) command at the beginning of an SMTP session (default enabled).
Note
Enabling this will stop some UCE malware.
- Reject invalid hostname
Reject the connecting client when the client HELO or EHLO parameter supplies an invalid hostname (default enabled).
- Reject non fqdn sender
Reject the connecting client when the hostname supplied within the client HELO or EHLO command is not a fully-qualified domain name, as required by the RFC (default enabled).
- Reject non fqdn recipient
Reject the request when the RCPT TO address is not in fully-qualified domain form, as required by the RFC.
- Reject unknown sender domain
Reject the connected client when the sender mail address has no DNS A or MX record (default enabled).
- Reject unknown recipient domain
Reject the connected client when the recipient mail address has no DNS A or MX record (default enabled).
- SMTP Helo Name
The hostname to send with the SMTP EHLO or HELO command. The default value is the IP of RED. Specify a hostname or IP address.
- Always BCC Address
Optional address that receives a blind carbon copy of each message that is received by the SMTP proxy system.
Note
If the e-mail to the BCC address bounces it will be returned to the sender.
- Smtpd hard error limit
The maximal number of errors a remote SMTP client is allowed to make without delivering mail. The SMTP Proxy server disconnects when the limit is exceeded (default 20).
- Language E-Mail Templates
Allows to specify the language for the error messages (default English).
- Maximal E-Mail size
The maximal allowed size (in MBytes) a message can have (default 10MB).
- Save changes and restart
Save the settings and restart the SMTP Proxy by clicking the save changes and restart button.
This page was last modified on: $Date: 2006-11-23 19:30:06 +0100 (Thu, 23 Nov 2006) $.